
Even if you are capable of protecting your personal security well, it doesn’t mean that your business will be safe, too. The thing is, companies are constantly being on hackers’ radar.
As a business owner, you are responsible for storing financial and personal data of your clients, partners, and employees. Penetrating a personal device gives access to a very limited amount of information while infecting business websites or work devices has a much bigger scope.
Just a small tip on security basics before we start. If you have a small business, go to a Avast free antivirus download page – a free solution will be enough. However, if you are working with dozens of people, getting a safe paid solution is a sensible thing to do.
Type #1 – DOS and DDOS attacks
DOS attacks are most dangerous to website owners rather than to their visitors. If you have an online shop or a blog, read this section carefully.
If your website became a target of a DOS attack, it means that users will not be able to access it. Whenever someone tries to open a web page, the server will send an error message. It looks as if the server has been overloaded. However, it’s not due to the website’s popularity but because the page has become a target of a malicious server overload, also known as a denial of service.
Luckily, now network protocols block the possibility of overloading a website from a single server or device. To cause the denial or server, the attacker needs at least dozens of servers – and hackers cannot usually allow such luxury. Still, it remains a possibility.
A DDoS attack is stronger and more difficult to counterattack. Precisely because hackers cannot target a website from one server, they are used to apply several servers and devices. If the hacker has access to several devices across the globe, he can use those resources in order to start a deliberate attack. An overload, performed from international servers, is harder to locate, and therefore, it takes a lot of time to return the website’s functionality back to is a normal level.
Type #2 – Man in the middle
In computer’s security, the saying about walls having ears is truer than in any other field. In fact, there exists a particular type of attack that is based on eavesdropping. Whenever you have a Skype conversation or chat via email, someone can intercept the dialogue.
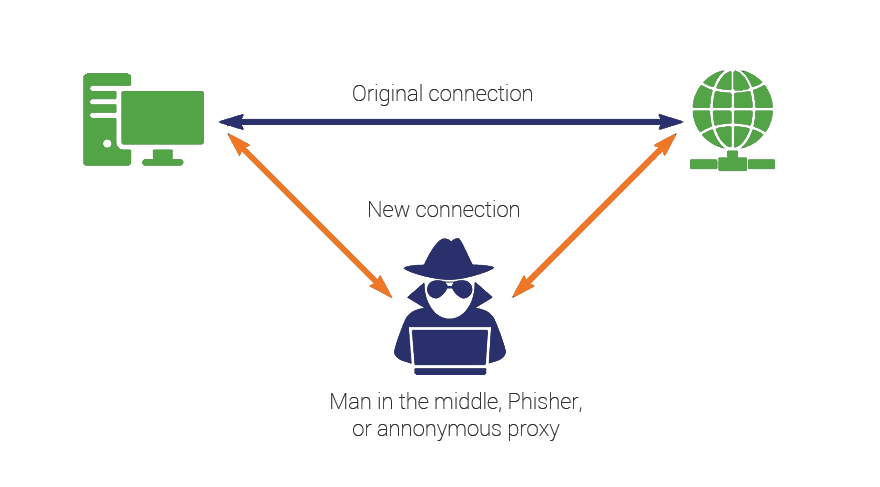
You never know about this man – but he knows about you.
Say, you want to talk to your client. So, a client sends you a message. The attacker uses this opportunity, takes over the message, alters it and sends it back to the receiver. Even if the message was encrypted (like in WhatsApp), the hacker will have to find the sender’s private key and use it in order to get access to the actual content.
The same procedure is repeated vice versa. This means, your message will, too, be overtaken and altered. Now your entire conversation is being spied on – and you have no idea.
To fight this threat off, use a secure VPN and have additional encryption. Even though the majority of the services use AES-256 encryption, there is no harm in adding an additional custom level of encryption. Install a tool that will encode your text messages and attachments. Voice messages can be protected by audio encryption tools.
Type #3 – Rootkits
A rootkit is a set of remote-control tools that allow accessing computers and networks remotely. Once the connection is secured, the rootkit may steal passwords, tap into financial data, peak into your emails, and compromise sensitive data.
Rootkits are known to disable antiviruses. You will never know that your security client stopped functioning. This leaves your computer opened to all kinds of security threats. Just like trojans, rootkits infiltrate themselves in otherwise secure software files. Also, they can be hiding in malvertising, emails, and infected links.
Enable a rootkit scan on your antivirus and delete the threat with your PC turned off. Just like spyware, rootkits tend to fight back – which is impossible to do when the Windows is not running.
Type #4 – Phishing
Phishing is based on deceitful communications where messages that appear trustworthy, ask your financial data, passwords, PIN-codes, locations, and others. The may come in the form of emails, registration forms, or malicious links.
Once you’ve opened the source of the threat, a file will be installed on your PC without your notice or approval. From now one, it will execute its main function – looking for sensitive data and giving it away to a third party.
Type #5 – SQL attacks
In case you were unaware, the majority of websites store the data on their users, products, even content in SQL databases. The information from your registration forms is sent directly to the database where it’s processed, collected and stored.
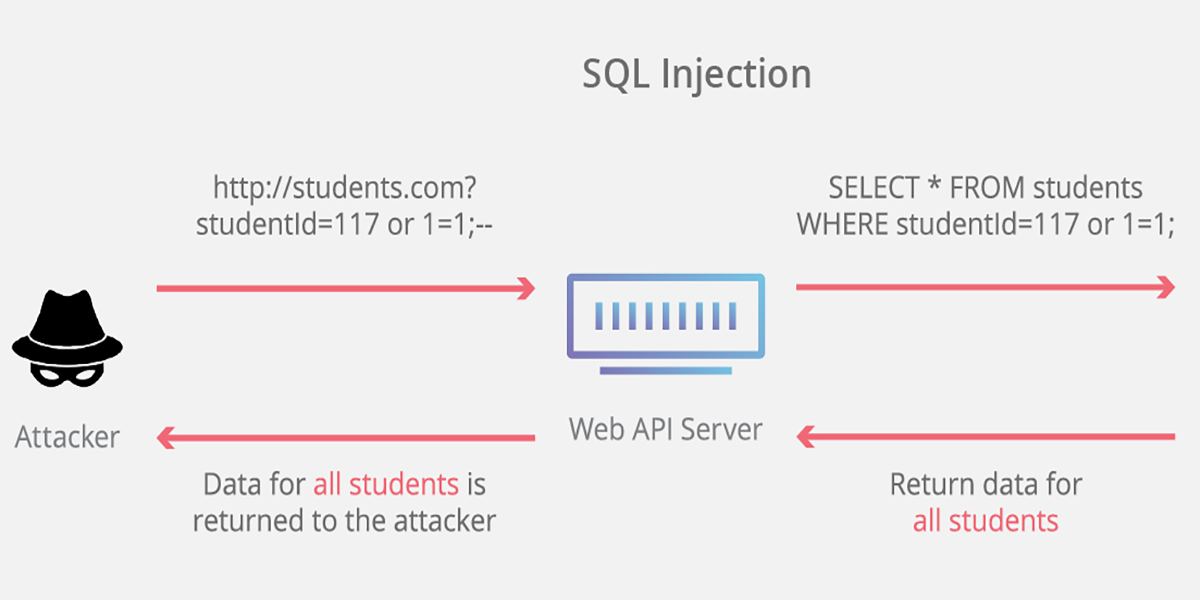
SQL-injections attacks are designed with the purpose of penetrating this database and receiving a lot of confidential data. For hackers, attacking a big database is the fastest way of receiving potentially valuable assets. If you have an SQL database, be sure to use dedicated business protections. The majority of antiviruses have special features for SQL protection in their Pro versions.
Conclusions
Even though antiviruses promise to provide their users with all-in-one protection, business owners need to go an extra mile to ensure their data’s safety.
Firstly, check your antivirus’ settings and make sure that all security layers are enabled properly. If you are frequently targeted with a particular threat, it’s worth to go an extra mile and download software, dedicated particularly to this type of risk. When you take responsibility for dozens of people, saving money and efforts on such important matter as security, is borderline reckless.








